Where to place the sockets in the bathroom

Even before the beginning of 2000, the outlet in the bathroom was banned, which was spelled out in the provisions of the PUE. With the advent of new materials and installation methods, some requirements have become more stringent, while others have become softer, as a result of which the outlet for the bathroom, although with a number of reservations, ceased to fall into the category of prohibited solutions.
Content
Bathroom zoning, according to the requirements of the PUE
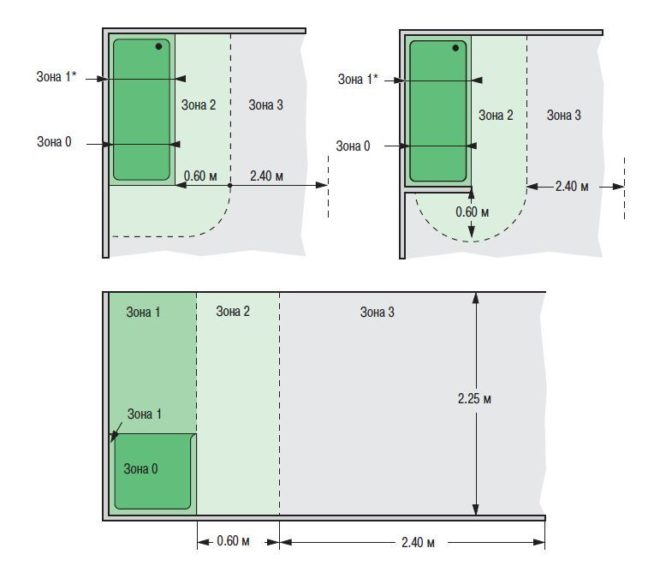
First of all, the reservations in question govern the place where the installation of an outlet in the bathroom is allowed. To do this, it is noted in the room where the bathroom, shower, washbasin or toilet will be installed - i.e. any object to which water is supplied through pipes.
- Each of the installation locations is considered the so-called "zone 0", in which the installation of sockets is strictly prohibited. It can use only those electrical appliances that are directly intended for the bathroom, are protected against water penetration and are powered from a voltage not exceeding 12 volts.
- The surface of the wall up and down from the zero zone is called "zone 1", in which any outlets are also excluded, but it is allowed to connect luminaires with an IP-x5 protection rating, which allows the device to withstand watering. The rules do not prohibit placing boilers here, but in practice they will only interfere.
- At a distance of 60 cm to the left and to the right of the dimensions of the first zone, there is “zone 2”. The installation of sockets is also prohibited here, but the installation of electrical appliances with an IP-x4 protection class is allowed, which allows the device to be exposed to rain. The location of zone 2 also depends on the presence of a stationary partition between the shower and the rest of the room. If it is, then the zone is calculated as a circle with a radius of 60 cm and centered at the extreme point of the partition.
- The distance of 2.4 meters from the border of the second zone is called "zone 3", which is considered a relatively safe distance to the water source. Here it is allowed to install 220 volt sockets with IP-x4 splash protection class and additionally equipped with appropriate protection.
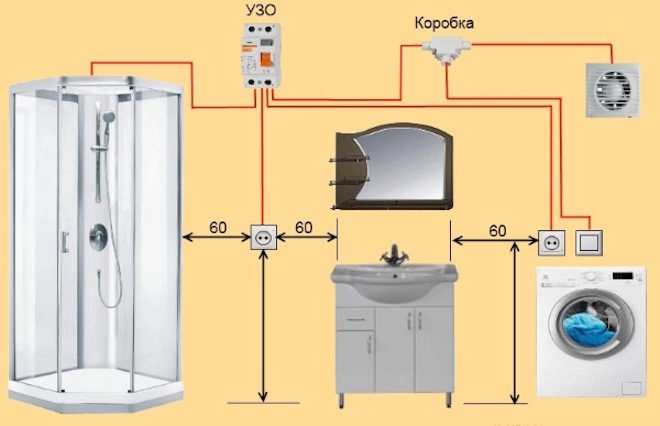
From these rules it is clear that if there is a shower cabin in the bathroom, and a washbasin is located a meter away from it, then you cannot put an outlet between them. In this case, it is allowed to hang up a boiler, which is directly powered by a wire from the mains or plugged into an outlet located in permitted zone 3. If mirror illumination is used, then the lighting lamps must be rated for a voltage not higher than 12 volts.
Where else is installation allowed
There are a few curious additions to the rules about zones in which you can or cannot place outlets. Each of them does not go all the way to the ceiling - the height of any of them is 2.25 meters. This means that if the ceiling height is 2.5 meters, then the location of the sockets in the bathroom may even be above zone 1, but at a height of 2.3 meters. Thus, the requirement to place the wiring 15 cm from the ceiling is additionally met.
This at first glance ridiculous rule allows you to "get out" of the situation and do everything according to the PUE when the room is small, and sockets are needed for stationary devices - the same boiler and washing machine.
Types of sockets according to the level of moisture resistance
Even if the outlet is located in the desired area and according to all the rules, it can still get splashed with water or condensation that will inevitably occur in the bathroom.Based on this, it is necessary to select waterproof sockets for the bathroom, the conductive parts of which are sufficiently protected from water ingress.

On any outlet, the manufacturer is obliged to affix the IP-XY standard marking, in which, instead of XY, numbers from 0 to 8 will be put down. The first of the numbers shows the protection of the mechanism from various objects falling into it, and the second shows the level of its protection from moisture:
- 0 - Contacts are not protected by anything - even from accidental splashes.
- 1 - The contacts will not be sprayed from above.
- 2 - Protection against drizzling rain when the slope of the spray does not exceed 15 °
- 3 - The device can withstand heavy rain with a splash slope of up to 60 °
- 4 - Contacts are splash-proof from all directions.
- 5 - This device can be watered with a hose.
- 6 - Protection for devices that can be affected by the wave.
- 7 - Protection against short-term immersion to a depth of one meter.
- 8 - Completely waterproof device.
The bathroom requires sockets and other electrical appliances with an IP-x4 or higher protection class.
Wiring requirements and number of outlets
The most powerful electrical appliances for which a power outlet is being installed in the bathroom are a boiler, a washing machine and a hairdryer. They consume about 1.5-3 kilowatts each, depending on the model. Additionally, devices such as a curling iron, an electric shaver and the like, which do not differ in high power, but require a separate connection, can be used here.

If the boiler is not directly connected to the network (some of them can only be powered in this way), then separate sockets are needed for it and the washing machine in any case - it is best if the wires to them are routed to each separately from the input panel (especially since junction boxes should not be installed in rooms with high humidity). Also, an outlet is needed near the washbasin - it is unlikely that several devices will be connected to it at once, but it is better if it is double.
As a result, no rules and regulations are imposed on the number of outlets - it is selected depending on how many devices are planned to be turned on.
The cross-section of wires that will be laid in the bathroom is taken at the rate of 2.5 mm² for sockets and 1.5 mm² for lighting - this should be sufficient with the above device power. Otherwise, the cross-section of the wires must be selected individually.
PUE strongly recommend to lay the wiring in a closed way - inside the wall. If for some reason it is necessary to lay wires along the surface of the wall, then firstly, you need to use a cable with the appropriate insulation class, and secondly, lay it in a polyethylene corrugated pipe. Metal can not be used, as in the event of a short circuit, it can lead to electric shock to a person.
Protection: grounding, RCD and isolation transformer
 The requirements of the PUE clearly indicate the need to use protective devices for outlets in the bathroom. Grounding and RCD are mandatory, the recommended one is an isolation transformer.
The requirements of the PUE clearly indicate the need to use protective devices for outlets in the bathroom. Grounding and RCD are mandatory, the recommended one is an isolation transformer.
The grounding conductor must be connected not only to outlets in the bathroom, but also to any other in the apartment or house. This is a guaranteed protection that protects a person from the effects of the phase on the body, which may appear on the metal parts of the cases of electrical appliances.
A circuit breaker cuts off the power supply in the event of a dangerous overload in the network.
The residual current device is triggered if a leakage current occurs, which occurs when a phase is shorted to the device case, connected to a socket with an earthing contact. There are ways to connect an RCD without grounding, but this protective device works most efficiently if the leakage current has somewhere to go.With the correct connection and selection of the protective device, the maximum trip current of the RCD is 30 mA.
The last of the listed devices, despite its usefulness, is practically not used, since it requires rather large investments both for the purchase of a transformer and for its installation. In fact, this is a standard transformer, but it does not increase or decrease the voltage, but leaves it unchanged. Its protective functions lie in the fact that the line that it feeds is not directly connected to the common circuit, and therefore there is no usual human connection with the earth in this case. As a result, a leakage current that may appear on the body of an electrical appliance when a phase breaks through it will not be dangerous for a person.
How is installation done

Except for the need to use waterproof devices, the installation of such an outlet in the bathroom is no different from the standard installation procedure. If closed electrical wiring is used, then it is necessary to calculate in advance in what place and how to make the sockets. At these points, holes are drilled for socket boxes and grooves are cut into the wall to them, where the wiring will fit.
Since the bathroom is always tiled, the wires are placed in the resulting hole and its location is carefully measured. When the tile is laid, a hole is drilled in it from which the wire is removed and an outlet is installed in this place.
If the finishing work has already been completed, but you need to add another outlet in the bathroom, then an open type of electrical wiring is used, which is laid in a plastic corrugated pipe or cable channel. The sockets themselves are screwed with dowels, for fixing which holes are pre-drilled in the tile.
What is the result
Considering the number of modern electrical appliances, a socket is also needed in the bathroom. The main thing in this matter is to choose the right place for its installation, choose a device with the appropriate class of moisture resistance and ensure the protection of the person himself from electric shock.
In the case when electricians from outside are invited to install the sockets, it does not hurt to ask them where and how to install these devices. If the masters do not care where to install them, then it is worth thinking about their qualifications and the need to receive such services.




